CRM vs. ERP: What’s the Difference for American Businesses?
In today’s competitive American business landscape, leveraging technology to streamline operations and enhance customer relationships is paramount. Two acronyms that frequently surface in discussions about business software solutions are CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). While both aim to improve efficiency and profitability, they address different core areas of a business. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of CRM and ERP systems, specifically tailored to the needs and understanding of American businesses, helping you determine which solution, or combination of solutions, is right for your organization.
Understanding the Foundations: CRM and ERP Defined
To understand the difference between CRM and ERP, it’s crucial to grasp their fundamental purposes and the areas they manage.
-
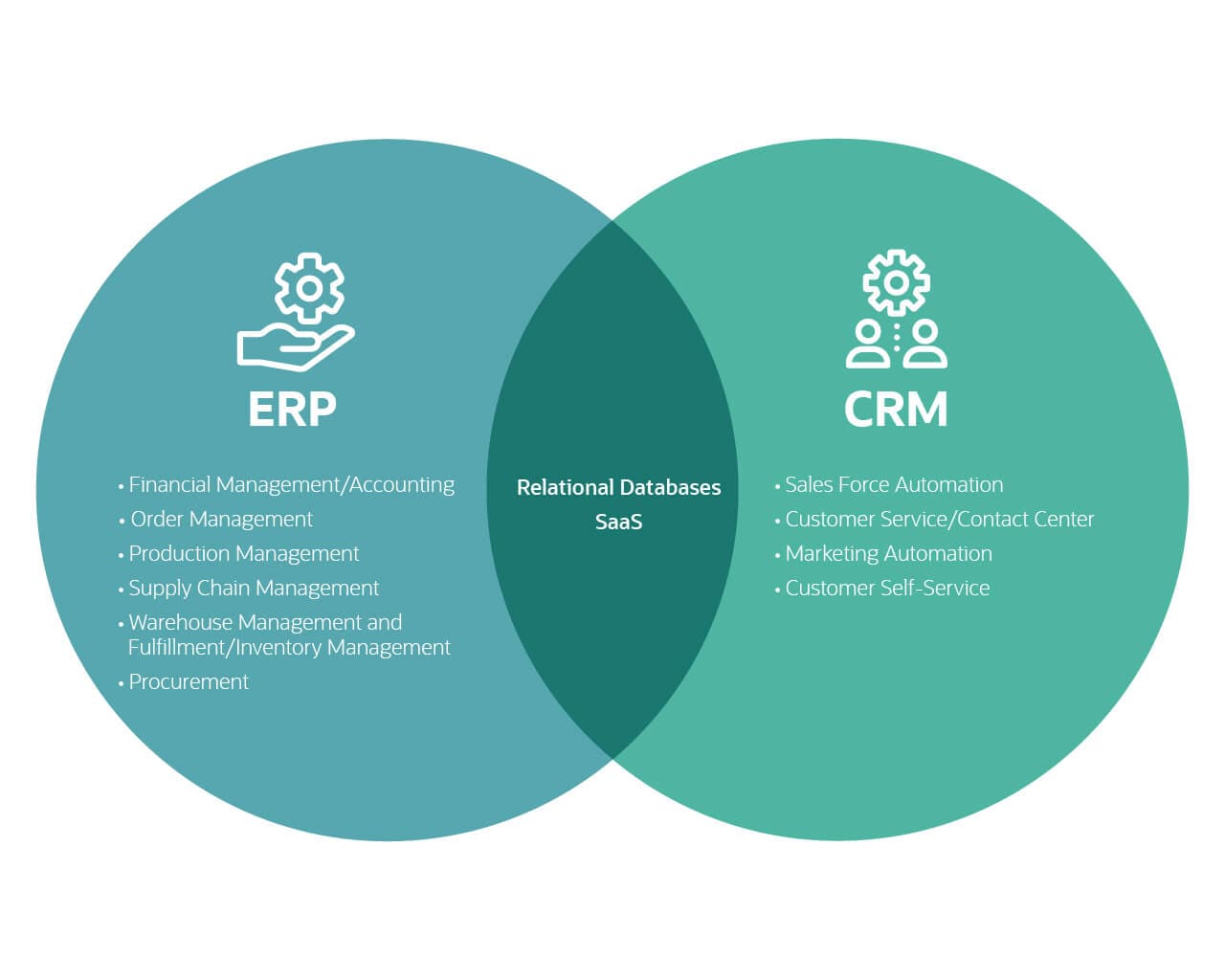
CRM (Customer Relationship Management): CRM software focuses primarily on managing interactions with customers and prospects. It centralizes customer data, allowing businesses to track interactions, manage leads, automate marketing campaigns, provide excellent customer service, and ultimately drive sales growth. Think of it as the hub for all things customer-related. Popular CRM platforms include Salesforce, HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales.
-
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): ERP software is a more comprehensive solution that integrates various business processes across the entire organization. It manages core functions like finance, accounting, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain management, inventory control, and project management. ERP aims to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide a centralized view of the business. Prominent ERP systems include SAP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations, and Infor.
Feature Comparison: A Side-by-Side Analysis
To illustrate the distinct roles of CRM and ERP systems, let’s compare their key features in a clear, concise chart:
| Feature Category | CRM (Customer Relationship Management) | ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Customer Acquisition, Retention, and Satisfaction | Internal Business Operations and Efficiency |
| Data Management | Customer Data (contact information, interactions, purchase history, preferences) | Operational Data (financial data, inventory levels, production schedules, employee information) |
| Key Modules | Sales Force Automation, Marketing Automation, Customer Service, Contact Management, Lead Management, Analytics & Reporting | Financial Management, Accounting, Human Resources, Supply Chain Management, Inventory Management, Manufacturing (if applicable), Project Management |
| Typical Users | Sales Teams, Marketing Teams, Customer Service Representatives | Finance Department, Operations Managers, HR Department, Supply Chain Managers, Production Managers |
| Primary Goal | Increase Sales, Improve Customer Loyalty, Enhance Customer Experience | Reduce Costs, Improve Efficiency, Streamline Operations, Increase Profitability |
| Reporting Focus | Sales Performance, Marketing ROI, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Acquisition Cost | Financial Performance, Operational Efficiency, Inventory Turnover, Production Costs |
| Integration Points | Marketing Automation Platforms, Email Marketing Tools, Social Media Platforms, E-commerce Platforms | CRM Systems, Supply Chain Partners, Banking Systems, Payroll Systems |
| Scalability | Highly scalable to accommodate growing customer bases and sales teams | Scalable to support expanding business operations and increasing data volumes |
| Deployment Options | Cloud-based, On-premise, Hybrid | Cloud-based, On-premise, Hybrid |
Use Case Scenarios: Bringing the Concepts to Life
Understanding how CRM and ERP systems are applied in real-world scenarios can further clarify their differences. Consider these examples:
-
Scenario 1: A Growing E-commerce Business
-
Challenge: An online retailer struggles to manage customer inquiries, track sales leads, and personalize marketing campaigns. Their inventory management is also becoming inefficient, leading to stockouts and delays.
-
CRM Solution: Implementing a CRM system allows the retailer to centralize customer data, track interactions, automate email marketing, and provide faster customer service. This leads to increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced brand loyalty.
-
ERP Solution: Implementing an ERP system helps the retailer manage inventory levels, track orders, automate shipping processes, and integrate with their accounting system. This improves operational efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures timely order fulfillment.
-
-
Scenario 2: A Manufacturing Company
-
Challenge: A manufacturing company faces challenges in managing production schedules, tracking inventory, and controlling costs. They also struggle to coordinate sales and production activities.
-
CRM Solution: Implementing a CRM system enables the company to track sales leads, manage customer orders, and forecast demand. This allows them to align production schedules with customer needs and improve sales performance.
-
ERP Solution: Implementing an ERP system helps the company manage production planning, track inventory levels, control costs, and integrate with their accounting system. This improves operational efficiency, reduces waste, and ensures timely delivery of products.
-
-
Scenario 3: A Professional Services Firm
-
Challenge: A consulting firm struggles to manage client relationships, track project progress, and bill clients accurately. They also face challenges in managing employee time and expenses.
-
CRM Solution: Implementing a CRM system allows the firm to manage client interactions, track project progress, and automate billing processes. This improves client satisfaction, enhances project management, and ensures accurate billing.
-
ERP Solution: Implementing an ERP system helps the firm manage employee time and expenses, track project costs, and integrate with their accounting system. This improves financial management, reduces administrative overhead, and ensures accurate reporting.
-
Pros and Cons: Weighing the Advantages and Disadvantages
Before making a decision, it’s crucial to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each system:
CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
Pros:
- Improved Customer Relationships: Centralized customer data and personalized interactions lead to stronger relationships and increased loyalty.
- Increased Sales: Effective lead management, sales automation, and targeted marketing campaigns drive sales growth.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Faster response times, personalized support, and proactive communication improve customer satisfaction.
- Better Marketing ROI: Track marketing campaign performance, identify effective strategies, and optimize marketing spend.
- Improved Data-Driven Decision Making: Access to comprehensive customer data and analytics enables informed business decisions.
Cons:
- Limited Scope: Primarily focuses on customer-facing activities and doesn’t address internal operational challenges.
- Data Silos: Can create data silos if not properly integrated with other systems, such as ERP.
- Implementation Costs: Can be expensive to implement and customize, especially for large organizations.
- User Adoption Challenges: Requires training and buy-in from sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
- Potential Privacy Concerns: Requires careful attention to data privacy regulations and security measures.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
Pros:
- Streamlined Operations: Integrates various business processes, eliminating redundancies and improving efficiency.
- Reduced Costs: Automates tasks, optimizes resource allocation, and reduces operational expenses.
- Improved Data Visibility: Provides a centralized view of business data, enabling better decision-making.
- Enhanced Compliance: Facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Improved Inventory Management: Optimizes inventory levels, reduces stockouts, and minimizes carrying costs.
Cons:
- High Implementation Costs: Can be very expensive to implement and customize, especially for complex organizations.
- Complex Implementation: Requires significant planning, configuration, and customization.
- User Adoption Challenges: Requires extensive training and buy-in from employees across all departments.
- Potential for Disruption: Can disrupt existing business processes during implementation.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating with legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming.
CRM and ERP Together: The Power of Integration
While CRM and ERP systems address different areas of a business, they can be even more powerful when integrated. Integrating CRM and ERP allows for seamless data flow between sales, marketing, operations, and finance, providing a holistic view of the business.
Benefits of CRM and ERP Integration:
- Improved Sales Forecasting: Access to real-time inventory data and production schedules enables more accurate sales forecasting.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Customer service representatives can access order history, inventory levels, and shipping information to provide faster and more informed support.
- Streamlined Order Management: Automated order processing and fulfillment reduce errors and improve efficiency.
- Better Inventory Management: Sales data informs inventory planning, preventing stockouts and minimizing carrying costs.
- Improved Data Visibility: A centralized view of customer and operational data enables better decision-making across the organization.
Summary Verdict: Choosing the Right Solution for Your American Business
Ultimately, the choice between CRM and ERP depends on the specific needs and priorities of your American business.
-
Choose CRM if: Your primary focus is on improving customer relationships, increasing sales, and enhancing customer service. You need a solution to manage customer data, track interactions, automate marketing campaigns, and provide personalized support.
-
Choose ERP if: Your primary focus is on streamlining internal operations, reducing costs, and improving efficiency. You need a solution to manage finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain management, and inventory control.
-
Consider Integrating CRM and ERP if: You need a holistic view of your business and want to leverage the benefits of both systems. Integration allows for seamless data flow between sales, marketing, operations, and finance, enabling better decision-making and improved overall performance.
For many American businesses, especially those experiencing growth or facing complex operational challenges, a combination of both CRM and ERP, ideally integrated, offers the most comprehensive and effective solution. By carefully evaluating your specific needs, considering the pros and cons of each system, and exploring integration options, you can make an informed decision that will drive growth, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Before making a final decision, consider these additional factors relevant to American businesses:
- Compliance Requirements: Ensure the chosen system complies with relevant U.S. regulations, such as GDPR (if dealing with European customers), HIPAA (if in healthcare), and SOX (if publicly traded).
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Look for CRM and ERP systems tailored to your specific industry, as they often include specialized features and functionalities.
- Vendor Reputation and Support: Choose a reputable vendor with a proven track record and excellent customer support, as implementation and ongoing maintenance are crucial for success.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Select a system that can scale with your business as it grows and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including implementation, customization, training, and ongoing maintenance, to ensure the solution is cost-effective for your business.
By taking these factors into account, American businesses can confidently select the right CRM and ERP solutions to achieve their strategic goals and thrive in today’s competitive market. Remember to prioritize a thorough needs assessment and involve key stakeholders in the decision-making process to ensure a successful implementation and maximize the return on investment.